
A fixed asset accounting policy aims to track the cost of a company’s fixed assets. Depreciation is a fundamental aspect of fixed asset accounting, reflecting the gradual reduction in value of an asset over its useful life. This process not only aligns the expense recognition with the revenue generated by the asset but also provides a more accurate picture of an organization’s financial health. Various methods can be employed to calculate depreciation, each with its own set of advantages and applications, depending on the nature of the asset and the organization’s financial strategy. Real estate or procurement teams should notify accounting when fixed assets fixed asset accounting process are purchased. Operations teams must notify accounting of any material changes to the asset such as damages or planned improvements.
Financial statement treatment of fixed assets
- By incorporating these expenses, you arrive at the total amount you spent on acquiring the asset.
- This information can be used in the filing of financial statements and tax returns.
- One key aspect of these standards is the requirement for detailed disclosures in financial statements.
- Utilizing specialized software like SAP Fixed Assets or Oracle Asset Management can streamline this process by automating data comparisons and generating reconciliation reports.
- A fixed asset may be transferred between subsidiaries, business segments, locations, or departments of an entity.
These factors might affect the property’s price depending on the property type. Depending on the type of asset, depreciation accelerates through depreciation recapture, which can increase the tax savings the company receives. However, depreciation is only a rough estimate of the total cost of an asset, so it’s essential to have a professional perform an accurate appraisal before it’s too late.

Explaining Asset Life Cycle and Its Organizational Structure to Represent a Fixed Asset
Audits can identify discrepancies, prevent fraud, and improve asset management. The reconciliation process also involves verifying the accuracy of depreciation calculations and ensuring that all asset additions, disposals, and impairments are correctly recorded. Utilizing specialized software like SAP Fixed Assets or Oracle Asset https://parquemetropolitano.com.co/2021/03/15/best-careers-for-the-future-jobs-for-2025-and-way/ Management can streamline this process by automating data comparisons and generating reconciliation reports.

Fixed Asset Reporting Standards
These assessments should be part of your routine accounting efforts, whether you’re following a simple accounting plan or are using a project-based accounting method. The asset’s cost is $20,000 and the salvage value is $4,000 which calculates to a depreciable base of $16,000. To learn about the role of the asset class, Kevin watches the following video. The non-integrated asset acquisition has already been tested successfully by the Asset Accounting department.
- An understanding of what is and isn’t a fixed asset is of great importance to investors, as it impacts the evaluation of a company.
- An older average age may indicate the organization will require reinvestment in fixed assets in the near future.
- These practices include regular audits, proper documentation, and the use of technology.
- The percentage is then multiplied by the asset’s depreciable base, cost less salvage value, to arrive at the depreciation to be recognized each period.
- Discover what asset management is, why it’s essential, and how to implement a secure and scalable strategy across your organization.
- Depreciation expense is recorded on the income statement to represent the decrease in value of fixed assets for the period.
The units of production method ties depreciation directly to the asset’s usage, making it ideal for machinery and equipment whose wear and tear are closely linked to operational output. This method calculates depreciation based on the number of units produced or hours operated, providing a more accurate reflection of the asset’s consumption. For instance, if a machine is expected to produce 100,000 units over its lifetime and costs $200,000, the depreciation expense per unit would be $2. This method ensures that depreciation aligns with actual usage, offering a more precise allocation of costs.
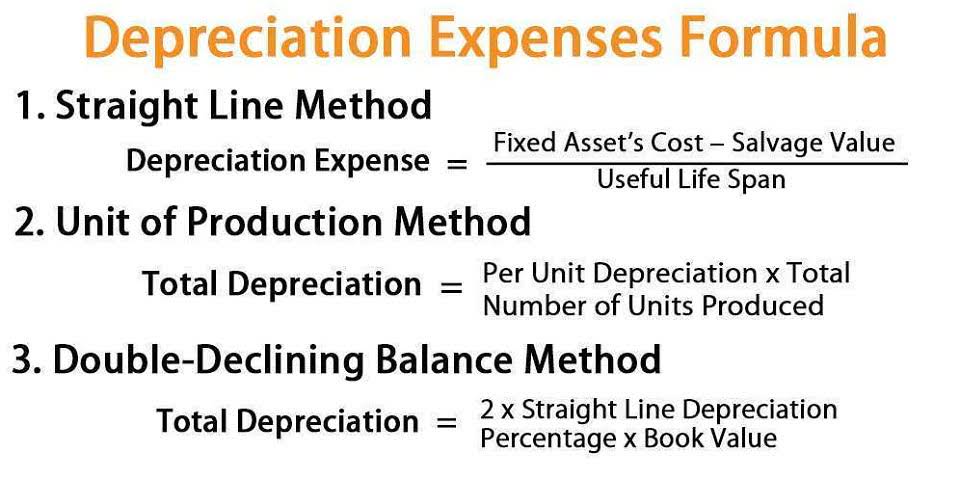

This ratio demonstrates a company’s ability to generate cash from operations to cover capital expenditures. Similar to the fixed asset turnover ratio, the CapEx ratio focuses on cash flows rather than using an accrual-based metric, revenue. A ratio greater than one means the organization generated enough operating cash to cover capital purchases. Various methods may be elected by organizations to depreciate fixed assets.
Declining Balance Method

In the case of asset grouping, one or multiple assets included in an asset group may be transferred. The treatment of operating lease ROU assets, however, is quite different from fixed assets and the related ROU asset is amortized using a different method. This means that in order to separate the data in reporting in General Ledger Accounting by asset class, there’s no need to create a new account determination for a new asset class. These different valuation approaches are displayed using depreciation areas (and ledgers) in the asset master record. For this reason, the control parameters and default values (see Asset Class) for the depreciation calculation are always normal balance displayed at the level of the depreciation area of an asset. To be able to manage values in the Asset Accounting for a fixed asset, an asset master record is needed.